Putting Common On-page SEO techniques to the test.
If you’ve ever wondered whether on-page SEO tips that experts recommend actually work, then you’ve come to the right place because we’re going to break down the top on-page SEO techniques that you can use to get higher rankings in Google, backed by hard cold data from Ahrefs from this study where they studied We studied 2 million random keyword searches.
On‐page SEO today is less about gaming the system and more about providing quality content. Your primary aim should be to fulfill search intent and give searchers what they want and are looking for. That’s the most important step. If you don’t pull that off, no amount of “optimization” will help you rank.
In this article, we’re going to be breaking down the top on-page SEO strategies and providing takeaways to boost your organic Google rankings.
You’ll also learn about some highly praised on page Google ranking factors that showed negative a correlation in the study (and what you should do instead).
Here at Rebel Zoom Digital, Ahrefs has to be one of our favorite SEO tools. They conduct in-depth case studies and provide actionable SEO tutorials that show you how to increase your organic search traffic and rank #1 on Google.
Top 10-page ranking factors this article will cover:
- Use short, keyword relevant URLs for your pages
- Use your primary keyword in your URL
- Use your keyword in the headline (H1 tag)
- Add external links to authoritative websites
- Add internal links to pages that you want to rank.
- Re-optimize titles on underperforming page 1 rankings
- Create in-depth and useful articles
- Use modifiers in your titles
- Optimize your web pages to load quickly
- Pay close attention to user experience
The one core key to always remember is: do what is most user friendly for people and most accessible for Google to understand.
10. Use short, keyword relevant URLs for your pages
Here are examples of what a short (good) URL looks like compared to an unnecessarily long URL (not good).

There has been debate whether long or short URLs are better for SEO.

In the above study on on-page SEO factors, we can see that on average, short URLs with a median of around 17 or so characters ranked visibly better than long ones.
Depending on what platform your website is built on, changing your URL can be pretty straightforward. If you’re a WordPress then all you need to do is click in the URL box and enter in your short URL as shown here.
Important Tip: Whenever you change the URL of an existing page, remember to add a redirect rule from the URL to the new one.
But does this mean that you should go and change all of your long URLs to short ones?
We wouldn’t say so. Even though there’s a small correlation, it’s not a significant enough ranking factor to change your existing ranking pages.
What you should be focusing on, and what the video above doesn’t really explain, is creating keyword-rich URLs that clearly indicate what the content on the page is about and add value to the page. Plenty of websites rank very well with blog posts that have the same words in their URL as their post title. Take, for example, the article we linked to about how to add a redirect rule to your website:

If you’re using long URLs where the length isn’t adding any extra value, consider cutting superfluous (see what we did there?) words.
9. Use your primary keyword in your URL
Compare these two URLs:
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322345.php
- https://www.dietdoctor.com/how-to-lose-weight
Which would you say is the more useful and user-friendly one? Just by looking at the URL of the second link, it’s easy to tell what the page is about, which is why is carries more relevance than the random numbers used in the first URL.
Descriptive URLs are good because they help you instantly know what you can expect from a page even before you open it.
There are a few reasons why this is good practice for on‐page SEO:
Firstly, as we discussed in the previous point, searchers are most likely to click the search result that best matches their search query. Descriptive URLs help cement your page as that result.
Secondly, and more importantly, descriptive URLs tend to include the keyword(s) you’re targeting. According to our previous study of 2M keywords, there’s a slight correlation between rankings and keywords in the URL.
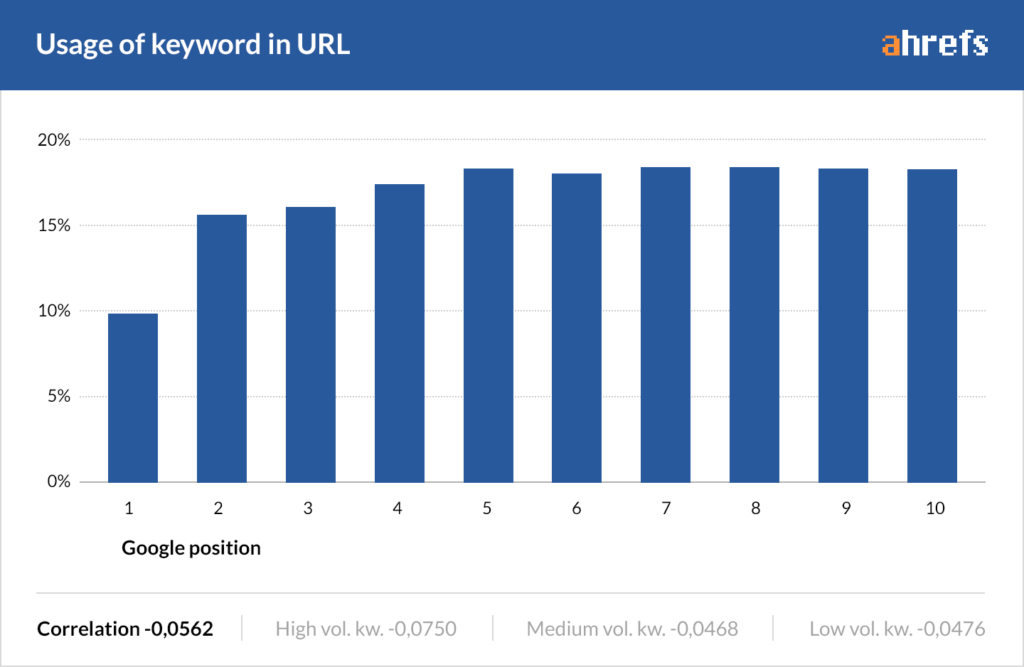
But what if your current URL structure doesn’t allow you to create descriptive URLs like this? Should you set about restructuring your entire site?
Here’s what Google’s John Mueller said about that:
I believe that is a very small ranking factor. So it is not something I’d really try to force. And it is not something I’d say it is even worth your effort to restructure your site just so you can get keywords in your URL.
Thing is… how often do you actually see links like this on the first page of Google?
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322345.php
Short answer: you rarely do. Pages like this are more likely to rank better:
- https://www.dietdoctor.com/how-to-lose-weight
(It’s always good to take SEO tips coming from Google with a pinch of salt – it’s in their best interests not to make it too easy for us to figure out their algorithm.)
Actionable takeaway: Aim for short and sweet URLs that are as descriptive as possible. Bonus points if you can include your target keyword in there (without it looking weird) and DO NOT KEYWORD STUFF YOUR URLS!
8. Use your keyword in the headline (the H1 tag)
One of the most common issues we see when analyzing new websites is where web designers have used heading tags for styling.
Pro Tip: If you’re a web designer – STOP DOING THIS. Consider using CSS or ID tags for styling purposes instead. Do NOT use heading tags for format text to look pretty on your website.
The purpose of heading tags is to help sort the hierarchy of content. How your content is structured helps both readers and search engines better understand what is more important. This then logically points to it making sense to try include your primary keyword – or at least a variation of it – in your main headings on your website.
Of course, a page can rank for multiple terms, meaning that not all pages will feature keywords they rank for in their titles, but it definitely helps.
The study by Ahrefs found that around 85% of pages that rank in the top 10 of Google don’t have their keyword in their H1 tags. However, there was still a noticeable correlation, so we still recommend using various keywords in your headings and even subheadings.

Most importantly, remember our golden rule: focus on the user experience.
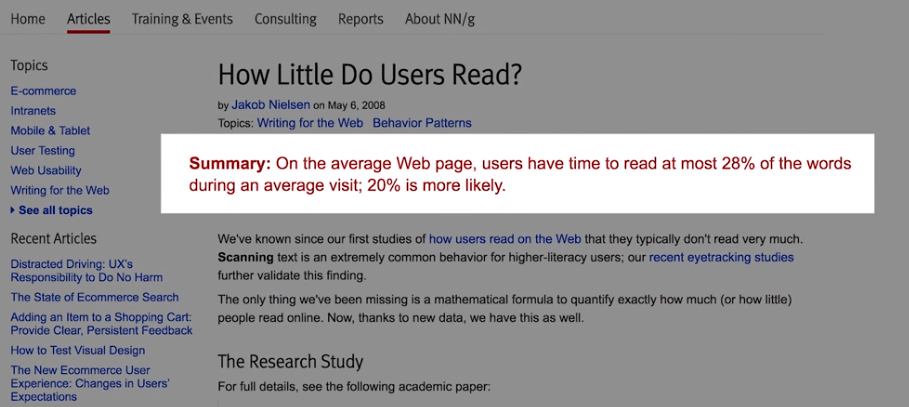
A study from found that on average, a user will read, at most, 28% of the words on a page, that 20% is more realistic.
Here’s the thing:
Scanning text is an extremely common behavior for users. You probably look at a page, scroll for a bit, and if something pops out to you, you read that section.
And if you think that section was awesome, then you think:
oh shoot, did I miss out on anything else?
So you scroll back up and then you read the post.
Using trigger-like keyword phrases in headings and sub-headings may be enough to pique a user’s interest and have them stick around a little bit longer.
7. Add external links to authoritative websites
Many websites are afraid to link out for fear of ‘losing’ traffic to the resources they link out to. But then you’re essentially turning your content in to a dead end, which isn’t really helping anyone.
Google’s John Mueller said that adding external links to other sites is not a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm.
Buuuuut… our own data, as well as this excellent report by Reboot Online disagrees where they ran a fun little experiment on these two completely made words: “Phylandocic” and “Ancludixis”.

They set up 10 different websites, 5 that linked to authoritative sources like Oxford, Cambridge, and genome.gov.
And then the other 5, they had no external links at all.
And the results were clear: the sites that contained external links, ranked higher than the ones that didn’t for both keywords.
In the Ahrefs study, there was a small positive correlation of pages that link to Domain Rating 70+ sites ranked in the top 10 of Google.

So here’s an easy takeaway: Don’t be afraid to link out to other resources that will enhance the experience for your readers.
For example, if you’re writing a blog post on the best golf gear and you found a great comparison of golf balls, then link out to them.
But don’t just do it for the sake of it.
6. Add internal links to pages that you want to rank
Internal links are links that go from one page on a domain to a different page on the same website. And these have been proven time and time again to help with rankings.
So a quick tip is to look at your pages that are currently ranking on page 2 of Google, add some internal links to relevant pages that you want to rank, and hopefully it’ll be enough to give your pages a small boost in rankings.

You can find pages that rank on page 2 by going to Google Search Console, click on search traffic, and then search analytics. Then make sure you check these boxes up here, and then sort the positions in descending order.

You can quickly scan through the impressions column and try to spot bigger numbers, which suggests that there’s a higher search volume.
Just bear in mind that these are average positions, which isn’t very accurate.
How to Use Ahrefs Explorer to find best inner pages to link to
- Go to https://ahrefs.com/site-explorer
- type in your domain or a subfolder and run the report
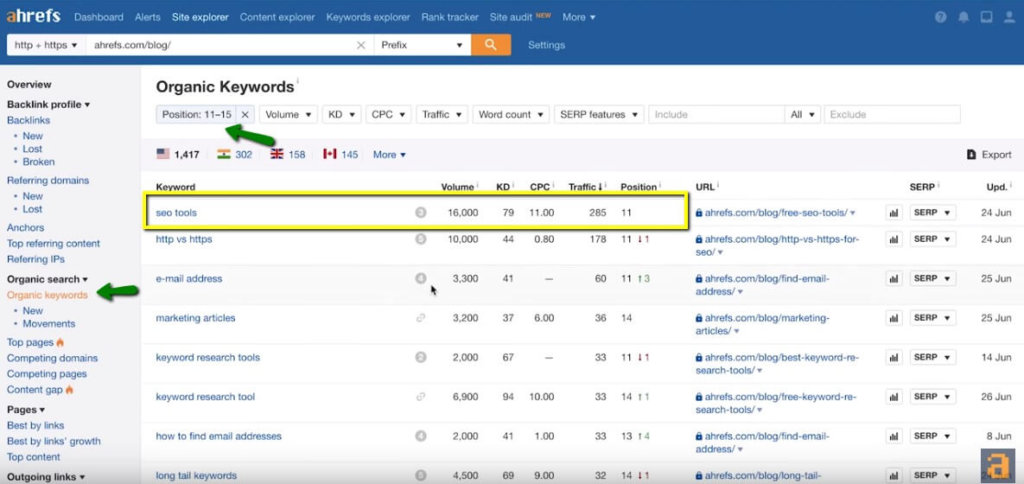
- Next, go to the Organic Keywords report, which will show you all of the keywords that ahrefs can see you rank for
- Narrow down our results by setting the positions filter to only show keywords that rank in positions 11 to 15. These pages would make for a great target to point some internal links to.
Now we need to find pages where we can add these links:
- Go to Google and type this search
query string:
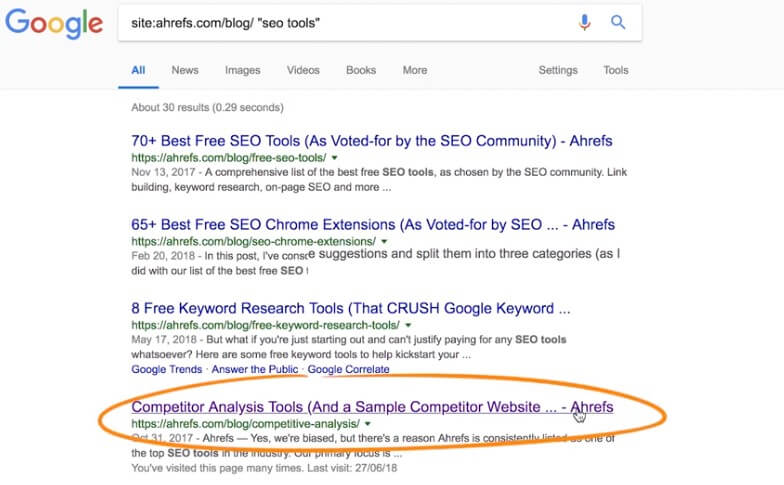
Site:yourwebsite/blog and add your keword in quotes for a phrase match search
Example – site:ahrefs.com/blog/, and add “SEO tools” in quotes - These pages on your website already contain that keyword in their content, so would be a great place to add the link.
5. Re-optimize titles on under-performing page one rankings
I’ll level with you: even if you have the perfect title and meta description combination, it won’t really matter much unless you’re on the first page of Google.
Why?
Because as the saying goes: “The best place to hide a dead body is on page 2 of Google’s search results.”

First, you need to identify the pages that are ranking on page one.
Again, you can do this in Google Search Console and look through the different positions versus click-through rates.
And as a very general benchmark, the #1 ranking spot sees an average CTR of 33%, #2 gets 15% and #3 gets around 10%.

If you see anything below that, make a note of it and start playing around with your titles and meta descriptions.
Here are a couple ways to get some great ideas for new titles:
Let’s say that I’m creating an epic post on hotels in San Francisco. Looking at the organic Google search results, you can see that they appear to be mostly list posts of the top or best ones. And two of them actually include prices in the title.

This can tell you a lot about the intent behind a searcher’s query. So you might want to create yours in a similar way.
Next, look at the ads.
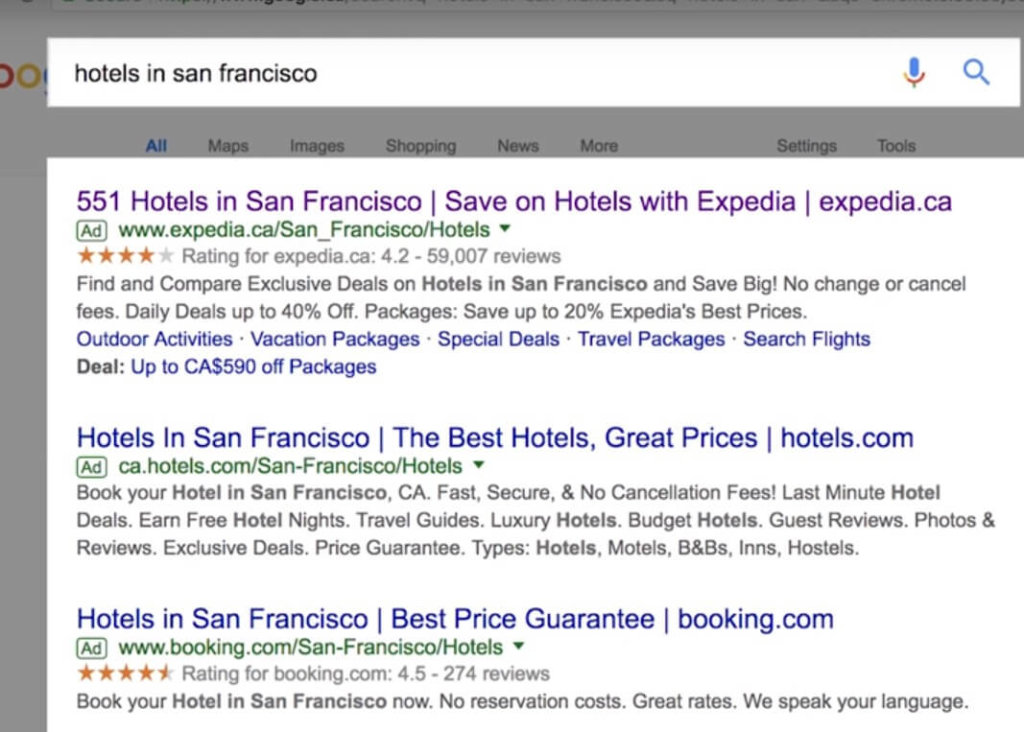
Since a lot of the big players are constantly experimenting with ad copy, you can bet that for high CPC terms like this, you’ll find some solid title and description ideas that can boost your CTR.
Easy data-driven way to use Google AdWords copy to optimize titles:
- Choose an Ad and copy the page’s URL without the parameters
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer tool and paste the URL here and run the search
- After the page loads, click on “ads” under the paid search category
- And right away, you can see all of the different ad variations and see which ones have been attracting the most clicks for them.

You can also borrow some ideas from viral sites like Upworthy or Buzzfeed:
For example, if I do a google search for site:buzzfeed.com “San Francisco” hotels, you’ll see a few cool ideas that you can work into your title tag.

4. Create in-depth articles
People have been raving about “long-form content” for quite some time.
In the graph below, you can see that, according to Ahrefs, content length has the second best correlation across all on-page SEO factors that they studied:

So how long is “long-form?”
1,500? 2,000? 5,000 words?
In the graph below, we can see that the median value for a #1 ranking result to have 800 words, which doesn’t quite fits into the category of “long-form.”
The reason long-form content has such a good rep is because of coverage and relevancy. Thing is, you could write a 10,000 word article. But if it’s no good, provides not value, or is riddled with errors that chase people away, it doesn’t matter how long your content is.
So instead of focusing on word count, focus on coverage.
For example, if you’re writing a piece on making the perfect cup of coffee, you can’t just say, say: “grab a cup, put it in the machine and wait.”
If you truly want to deliver on making the perfect cup of coffee, you’d want to talk about beans, water temperature, brewing methods like French press, drip, or using an Aeropress.
An easy way to find related subtopics is to Google the keyword phrase you want to rank for and skim through the sub-headings from the top ranking pages.
So what’s the bottom line?
Forget word count and focus on covering the topics and sub topics that will serve the searcher’s intent.
3. Use modifiers in your titles
Modifiers are add-on words to a base keyword. Some excellent add-ons are: best, top, buy, and the current year.

For example, someone might search for “golf clubs.”
But they might also search for “best golf clubs” or even “best golf clubs 2019.”
How to find modifier keywords with search volume in Ahrefs:
- Type in your seed keyword in
Keywords Explorer
Example: “Golf” - Next, go to the phrase match report in the sidebar
- You can see how many keywords exist
that have your seed keyword in it.
In this example, you can see that there are well over 2 million keywords with the keyword golf in it. - Next, click on the include search box and type in a modifier keyword like “best”.
- This will then show all seed keywords that contain your keyword modifier.
And you can see that there are some great keyword ideas where you can add modifiers to your title:

Best of all, for the golf niche, the keyword difficulty scores are extremely low on these, which makes them potentially great keyword targets that you can go after.
- Page speed – don’t have slow loading pages!
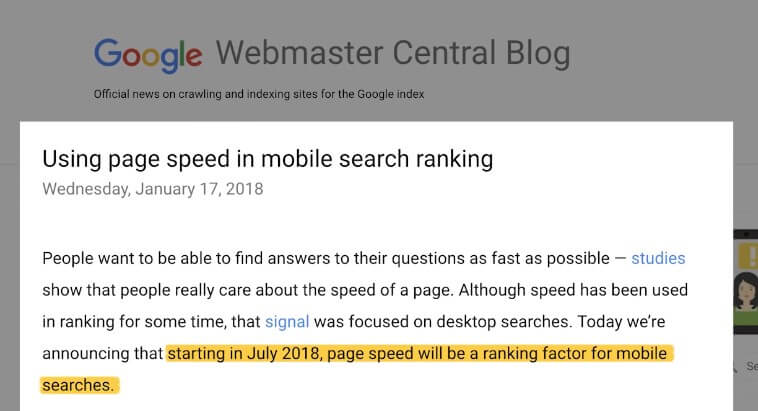
In 2010, Google announced a new signal in their search ranking algorithms: page speed.
And as of July 2018, page speed is a ranking factor for mobile searches:
But, according to Ahref’s research, the correlation of this on page factor with higher positions in Google considerably small.
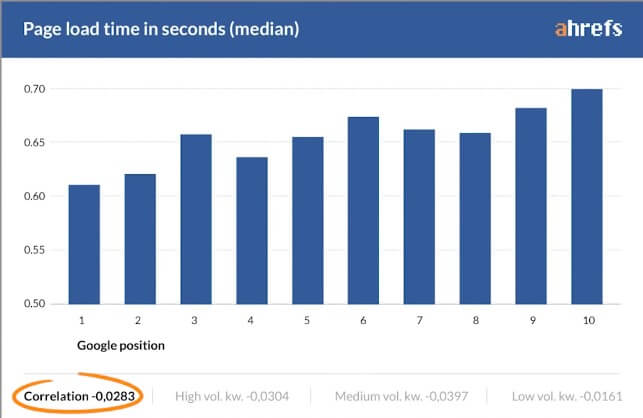
So should you even bother optimizing for page speed?
Absolutely!
This deals more with user experience and it will affect your bottom line: revenue.
Google performed a study on 11 million mobile ads and found that as page load time goes from 1 to 3 seconds, the probability of bounce increases 32%. And as the load time increases, so does the probability of bounce.

Tips to improve page load speed:
STEP 1: Google Page Speed Testing Tool
- First, go to Google Pagespeed Insights and enter in the URL that you want to analyze: https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/insights/
- Toggle between your mobile and desktop page speeds here.
- Scroll down a bit to see the optimization suggestions. (Often, you’ll see that slower page speeds are attributed to files like images, scripts, and style sheets.)
- If available, can click download optimized versions of these scripts, and style sheets which your web developer may be able to use as speed-optimized replacements on your page.
STEP 2: Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Next tip, use a content delivery network (or a CDN).

CDNs minimize the distance between where the visitor is browsing from and where your website server is hosted. For example, if your hosting server is located in New York, but your visitor is in Australia, it can take quite a bit of time for the transfer of data to complete. A CDN will help optimize the delivery of information so it doesn’t have to travel so far, speeding up response times.
Cloudflare offers a great free option to get you started: https://www.cloudflare.com/plans/
STEP 3: Image Compressor
The next tip is to use an image compressor and we do this because images in their raw form, they can be quite large.
At Rebel Zoom, one of our favorite image compression tools is Tiny PNG. They also have a WordPress plugin that will automatically compress images as you upload them to your site.

STEP 4: File Cache
Our final page speed tip is to cache, cache, cache! If you’re a WordPress user, you can use plugins like W3 Total Cache https://wordpress.org/plugins/w3-total-cache/ and get a solid configuration without a technical bone in your body.

And finally, we’re on to number one!
Are you ready for this?
1. Optimize User Experience!
This last tip almost summarizes all of the on page SEO factors into one, and is what we’ve been speaking about from the start: optimize your content to give users the best experience possible!
Google’s job is to provide the best results to their users for any given search query.
And in order to help Google achieve that, you need to foster that user experience for their visitors.
Aside from the content itself, the user interface, or the way the page looks, can have a significant impact on how people interact with your site.
If you look at these two pages side-by-side, which one is easier to read?

Obviously the first page on the left.
How to improve visual readability on your website:
- Use a readable font-size
- Write in short sentences and short paragraphs
- Include standout images connect with and engage readers and help them better understand concepts
- Avoid making your content too dense. Include headings, checklists, lists and pro tips to make your content hyper-scannable
- Have a table of contents for long posts (like this one)
- Consider relevant interactive features within your blog posts, such as a slide deck, videos, surveys and polls.
You can obsess over low-hanging optimizations like keywords in titles, but you need to know that there is power in cumulative value.
Now, while our data supports a lot of these on page SEO factors, there is very little correlation in most of our findings on an individual level. But, as you implement all of the different optimizations together, you should start seeing more results.
Most importantly, always focus on fulfilling the searcher’s intent the best you can and you’ll be on your way to perfecting your on-page SEO.
If you would like optimizing your website, please contact us to discuss what we can do for your website to drive more targeted traffic to it.

